- Prity Skincare Clinic
- Zinc Injection
Zinc Injection
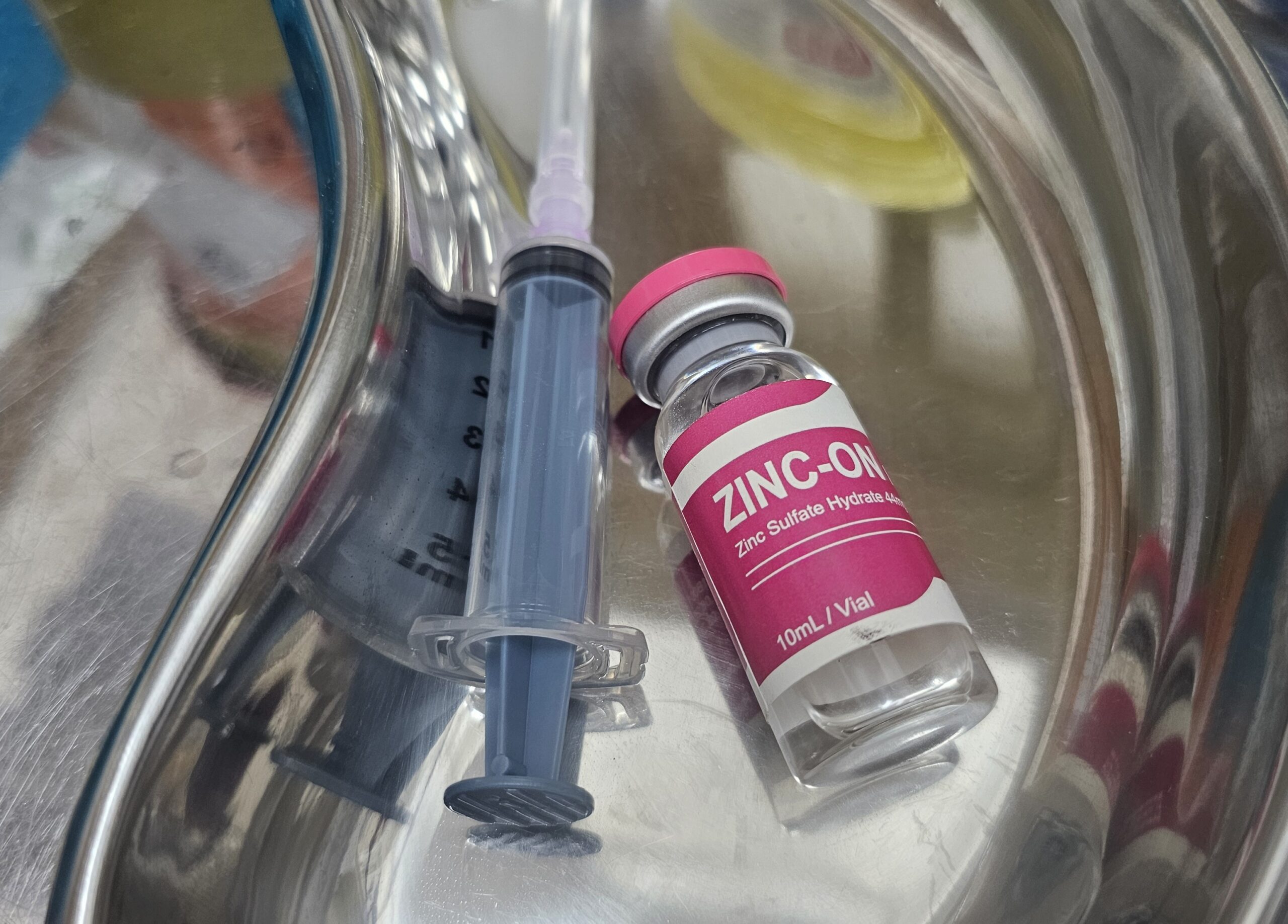

Zinc Injection
Zinc deficiency, a significant global health issue often stemming from inadequate diet or poor absorption, cause symptoms like hair loss, skin rashes, weakened immunity, and delayed wound healing. It is common in infants with certain genetic conditions and in people with chronic illnesses affecting the gut. It is treated with oral zinc supplements, although improving dietary intake is key.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Skin and Hair: Eczema-like rashes, specifically around the mouth, eyes, and buttocks, along with acne, hair loss (alopecia), and brittle nails.
- Immune System: Increased susceptibility to infections, such as colds, coughs, or chest infections, due to weakened immunity.
- Growth and Development: In children, it can lead to stunted growth and delayed development.
- Sensory and Appetite: Loss of taste, decreased sense of smell, and poor appetite (anorexia).
- Other Symptoms: Diarrhea, weight loss, delayed wound healing, lethargy, irritability, and, in men, decreased sperm production or low libido.
Zinc Injection
Zinc injections provide direct, rapid, and 100% bioavailable zinc to the body, bypassing the digestive system to treat deficiencies boost, immunity and enhance metabolic health. They offer critical support for wound healing, reduce inflammation, strengthen immune responses against viruses, and aid in treating chronic illnesses.
Key benefits of zinc injection:
Enhanced Immune System: Zinc injections help boost the production and action of immune cells, reducing the severity and duration of colds and flu.
- Rapid Healing & Tissue Repair: Due to potent anti-inflammatory properties, these injections are effective for accelerating wound healing and reducing tissue damage.
- Treatment of Deficiencies: Zinc sulphate injections are used to treat acute zinc deficiency, particularly in patients with gastrointestinal issues (e.g., severe diarrhea) that hinder oral absorption.
- Metabolic and Hormone Support: Zinc plays a key role in processing glucose and insulin, as well as maintaining hormone levels like testosterone.
- Improved Cognitive & Physical Function: Supports neurological functions, potentially improving memory and focus, while helping with energy levels and reducing recovery time from exercise.
- Organ Protection: High-dose, controlled intravenous zinc (HDIVZn) has shown potential in protecting organs, including the heart, liver, and kidneys, against injury.


